FACT YOU DIDN'T KNOW ABOUT WISDOM TEETH !!
Things you probably didn't know about wisdom teeth
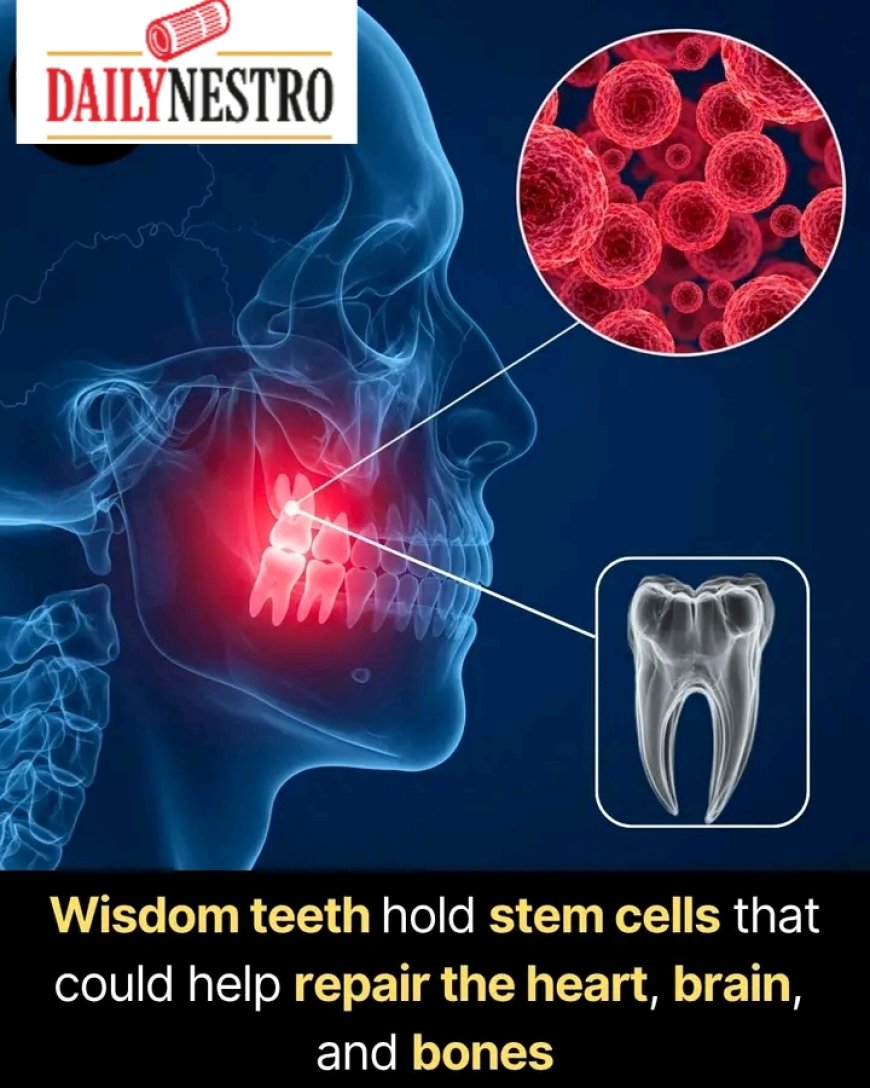
Are Wisdom Teeth More Valuable Than We Think?FACT YOU DIDN'T KNOW ABOUT WISDOM TOOTH
When we think about wisdom teeth, most of us imagine discomfort, swelling, and a scheduled surgery to have them removed. Dentists often recommend extracting these third molars to prevent crowding or future oral health problems. Once removed, they're usually discarded without a second thought.
But what if those unwanted teeth actually held hidden medical potential?
It turns out that wisdom teeth may contain valuable stem cells—specifically, dental pulp stem cells (DPSCs). These cells are found in the soft tissue at the center of the tooth and have remarkable regenerative properties. While they might seem like just another biological leftover, researchers now believe that DPSCs could someday play a critical role in personalized medicine.
What Are Dental Pulp Stem Cells?
Dental pulp stem cells are a type of mesenchymal stem cell found within the dental pulp—the innermost part of a tooth. These stem cells are capable of differentiating into a range of specialized cells, including:
▫️Bone cells (osteoblasts)
▫️Cartilage cells (chondrocytes)
▫️Fat cells (adipocytes)
▫️Nerve-like cells (neurons and glial cells)
This means that under the right conditions, DPSCs could help regenerate tissues damaged by injury, illness, or age-related degeneration.
Real Medical Potential, while in Early Stages
Although still in the experimental phase, early studies and lab trials have shown promising applications of DPSCs in regenerative medicine. Some of the most exciting areas of research include:
▫️Cardiac repair: Using DPSCs to help restore damaged heart muscle tissue after heart attacks
▫️Neurological treatments: Generating neuron-like cells that may one day be used to treat brain injuries or neurodegenerative diseases
▫️Bone and cartilage regeneration: Supporting healing in fractures, joint injuries, or bone loss due to medical conditions.
These breakthroughs are part of a larger movement in biotechnology focused on using the body’s own cells to repair itself — an approach known as "regenerative medicine"
Because of their accessibility, wisdom teeth are being explored as a potential source for stem cell banking. Just as some parents choose to store umbilical cord blood after childbirth, individuals may soon be able to store stem cells from extracted wisdom teeth for future use.
Companies and clinics are beginning to offer dental stem cell banking services, allowing patients to preserve these cells in specialized cryogenic storage facilities. While this is still a niche market, it represents a growing awareness of the untapped value in biological materials we often discard.
However, it’s important to note that these applications are still being researched. There are currently no mainstream medical treatments using DPSCs, and long-term clinical trials are still needed to but prove their safety and effectiveness. Still, the outlook is promising — and many scientists believe dental stem cells could be a powerful tool in the coming decades.
Conclusion:
Wisdom teeth may not seem like much — often painful, inconvenient, and quickly forgotten after extraction. But beneath the surface, they may hold one of the most exciting tools for future healthcare.
The sources: ledentistry and association ,







